The appearance of Anubis ransomware has stirred considerable concern in the cybersecurity community due to its unique and destructive capabilities. Discovered in late 2024, this ransomware variant has taken the concept of digital extortion to a new level by integrating a “wipe mode” into its operations. This mode can not only encrypt but also irreversibly destroy files on infected Windows systems, making any hope of recovering the data obsolete. Such functionality represents a significant evolution in the field of ransomware, as traditional ransomware typically encrypts data and demands payment for decryption keys. The introduction of Anubis suggests a troubling trend where attackers apply more intense pressure on victims to compel swift ransom payments by removing any possibility of negotiation or gradual recovery of files.
Technical Breakdown of Anubis Ransomware
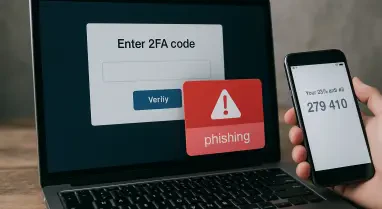
Anubis operates within the Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) framework, which allows cybercriminals to lease the ransomware to other attackers. This model broadens its potential reach and increases its distribution by lowering the barrier to entry for deploying attacks. The primary method of infiltrating systems is through phishing emails that are carefully crafted to imitate trusted sources, a tactic that increases the likelihood of successful penetration into target networks. Upon execution within a system, Anubis deploys additional payloads designed to carry out a series of malicious activities. These may include the removal of shadow copies, which are used by many systems as a backup to restore files, and privilege escalation, allowing attackers to gain elevated access to the compromised system’s resources.
Anubis has not yet reached a wide victim pool; however, its potential for widespread damage remains significant due to its novel destructive abilities. The innovative nature of its operations with the inclusion of the wiper functionality could serve as a model for future ransomware developments, forecasted to incorporate similar methods, emphasizing a shift towards more aggressive ransomware strategies. This shift marks a departure from ransomware tactics focused solely on encryption and underscores the importance of cybersecurity measures capable of tackling more aggressive and multifaceted threats.
Protecting Against Anubis and Similar Threats
To combat threats posed by Anubis and similar ransomware, cybersecurity experts stress the need for comprehensive protective measures. Among these, maintaining regular data backups is crucial, as it provides a reliable way to restore files without succumbing to ransom demands. This basic yet effective practice can significantly decrease the impact of ransomware attacks. User education is also pivotal, teaching individuals to recognize phishing attempts often used to distribute ransomware. Encouraging a culture of alertness and skepticism when handling unsolicited emails could prevent many attacks before they begin. Additionally, implementing robust internet safety measures, such as strong passwords and up-to-date antivirus programs, serves as a fundamental defense.
Organizations must remain vigilant and proactive, continuously updating and patching systems to mitigate vulnerabilities that ransomware like Anubis might exploit. Trend Micro, a notable cybersecurity entity, advises prioritizing these best practices to stay ahead of evolving threats. Given the ever-expanding and complex nature of ransomware threats, there is an urgent need for cybersecurity strategies that are equally dynamic and forward-thinking. The continuous development of threats like Anubis underscores the critical need for an adaptable security posture and the importance of staying informed about the latest in ransomware evolution.
A Call for Heightened Cybersecurity
Anubis functions within a Ransomware-as-a-Service (RaaS) model, enabling cybercriminals to rent out the ransomware to others. This approach significantly widens its potential impact by making it easier to launch attacks, as attackers no longer need to develop sophisticated malware on their own. The primary infiltration technique involves meticulously crafted phishing emails that mimic trusted sources, improving chances of success in breaching networks. Once executed, Anubis initiates a series of harmful actions using additional payloads. These actions often include deleting shadow copies, crucial for file restoration in many systems, and escalating privileges to gain higher access to system resources. While Anubis hasn’t yet targeted a large number of victims, its destructive capabilities suggest a high potential for widespread damage. Its innovative features, like the wiper functionality, could influence future ransomware, hinting at a trend toward more aggressive strategies. This evolution highlights the growing necessity for advanced cybersecurity to defend against such multifaceted threats.