The rising tide of data breaches in 2024 is reshaping the landscape for both consumers and industries, with significant consequences for personal privacy and corporate security. With a record-breaking start to the year, the Identity Theft Resource Center’s (ITRC) data shows that the alarmingly high number of publicly reported incidents indicates an unprecedented level of cybercriminal activity targeting valuable personal information. As cyberattacks become more sophisticated, industries are grappling with the increasing threat, and regulations are evolving to better mitigate these risks.
According to the ITRC, the sheer scale of data breaches in 2024 is on track to surpass previous records, with 841 publicly reported incidents in the first quarter alone. This number nearly doubles from the same period in the previous year, suggesting a troubling trend that could see the total breaches surpass 2023’s record of 3,203 incidents. The analysis highlights that these breaches are not only numerous but also impactful, with each incident exposing sensitive information such as Social Security numbers and affecting approximately 172,000 victims on average.
Industries Most Affected by Data Breaches
Hospitality Sector
One of the most concerning findings is the significant vulnerability of the hospitality sector to data breaches. Cybercriminals have increasingly targeted hotels and travel companies to access the personal and financial information of their guests. This sector heavily relies on digital systems for reservations and customer management, making it an attractive target for cyberattacks. The hospitality industry’s complex web of transactions, often involving multiple third-party service providers, further amplifies the potential attack vectors for cybercriminals.
From international hotel chains to local travel agencies, the hospitality industry has been grappling with the fallout of these cyber incidents. Breaches often result in not just financial losses but also a severe blow to a company’s reputation and customer trust. As new incidents continue to surface, industry leaders are called to implement more robust cybersecurity measures and conduct regular audits to safeguard customer data. The loss of guest information can lead to identity theft, fraud, and other long-term negative consequences for individuals, making the need for stringent security protocols more urgent than ever.
Financial Services
The financial services industry has emerged as the leading sector affected by data breaches in the first quarter of 2024, outstripping the healthcare sector for the top spot. Financial institutions, including banks and mortgage lenders, hold some of the most sensitive financial data, making them prime targets for cybercriminals. The largest data breach in early 2024 was at LoanDepot, a mortgage lender, exposing nearly 17 million victims. This incident marked the company’s second data breach since 2018, bringing its total number of affected individuals to an alarming 33.5 million.
Financial services organizations face a unique challenge due to the high value and sensitivity of the data they hold. Breaches in this sector can have sweeping ramifications, not only for the affected individuals but for the stability of the financial market itself. The increased occurrence of targeted attacks on financial institutions underscores the necessity for enhanced regulatory frameworks and industry-specific security standards. Financial service providers are now investing more in advanced security technologies and undertaking frequent risk assessments to fortify their defenses against growing cyber threats.
Healthcare Sector
The healthcare sector, although surpassed by financial services in the number of breaches, remains a significant target for cybercriminals. Healthcare organizations store vast amounts of personal and medical information, making them lucrative targets for data breaches. The sensitivity of the data held by healthcare providers means that breaches can have severe consequences, including identity theft and fraud. Additionally, compromised medical records can directly impact patient care and safety, leading to potential delays in treatment or incorrect medical management.
Healthcare data breaches are particularly debilitating because they involve information that cannot easily be changed, such as medical histories and treatment plans. The sector’s continued vulnerability indicates a pressing need for ongoing advancements in cybersecurity infrastructure. Healthcare providers are now increasingly adopting technologies like encryption, tokenization, and secure access protocols to protect patient data. Furthermore, increasing employee training on cyber awareness and best practices plays a pivotal role in mitigating risks and ensuring the security of medical records.
Trends in Cyberattacks
Targeted Attacks
A notable trend emerging from the analysis is the shift in cybercriminal strategies toward more targeted attacks. Rather than indiscriminately harvesting large amounts of data, cybercriminals are now focusing on specific kinds of valuable information. This tactical approach has resulted in a decrease in the number of victims per breach, even as the overall number of successful attacks continues to rise. Advanced malware, spear-phishing campaigns, and tailored exploitation methods are part of the evolving arsenal that cybercriminals are deploying to infiltrate systems with precision.
As hackers streamline their efforts to extract the most valuable data, organizations must also adapt their defensive measures to counter these sophisticated threats. Privacy experts suggest that the emergence of more targeted cyber threats is a sign that traditional security approaches may no longer suffice. Enhanced threat intelligence, ongoing monitoring, and rapid response capabilities are vital components of a modern cybersecurity strategy. Organizations must also promote a culture of vigilance and readiness, ensuring that employees are well-versed in recognizing and responding to targeted cyber threats.
Advanced Ransomware
Ransomware has evolved into one of the most formidable weapons in a cybercriminal’s arsenal, with attacks becoming increasingly sophisticated over time. Modern ransomware attacks do not merely encrypt data; they can also exfiltrate a victim’s sensitive information, doubly pressurizing organizations to pay ransoms to prevent public exposure of the stolen data. Such attacks lead to significant financial losses and operational disruptions, crippling organizations across various sectors and underscoring the importance of robust cybersecurity measures.
Organizations are now focusing on building resilience against ransomware by implementing multi-layered security defenses, comprehensive backup strategies, and regular system updates. Enhanced endpoint protection, network segmentation, and incident response planning are critical countermeasures to minimize the impact of ransomware attacks. By consistently practicing “defense in depth,” which involves a combination of preventive, detective, and responsive security measures, organizations can create a more formidable shield against the evolving ransomware landscape.
Vendor Exploitation
Vendor exploitation is becoming a growing concern in the cyberattack landscape, as cybercriminals target third-party vendors and suppliers to infiltrate larger organizations’ networks and data. This approach exploits the interconnected nature of modern business operations, where companies often rely on a network of external partners to deliver their services. Vendor exploitation highlights the necessity for companies to comprehensively secure not only their own systems but also those of their partners to prevent potential breach points.
The interconnected web of supplier relationships means that weaknesses at any single point can have a cascading effect, leading to widespread data breaches. Companies are encouraged to perform rigorous due diligence when selecting vendors, ensuring that their partners adhere to strict security protocols. Additionally, regular security assessments, thorough contractual obligations regarding data protection, and real-time monitoring of third-party activities are essential strategies that organizations must adopt to mitigate the risks associated with vendor exploitation.
Regulatory Landscape
Reporting Requirements
The evolving regulatory landscape plays a crucial role in understanding the scope of data breaches and implementing effective mitigation strategies. The Federal Trade Commission (FTC) has expanded reporting requirements for nonbanking financial institutions, mandating that breaches impacting 500 or more people be reported within 30 days of discovery. While these requirements represent a step forward, privacy experts argue that they fall short when compared to the stricter regulations in Europe, where companies must disclose breaches within three days.
Uniform and stringent reporting requirements are necessary to gain a clearer picture of the geographic distribution of data breaches and their victims. Experts suggest that transparency in breach disclosure not only helps regulators better understand the cyber threat landscape but also assists organizations in improving their defenses. Enhanced reporting standards can drive the creation of more actionable threat intelligence, enabling industries to adopt proactive measures to prevent future attacks.
Federal Privacy Legislation
A recurring theme throughout the analysis is the pressing need for comprehensive federal privacy legislation to address gaps in current laws and to improve data breach notifications. While individual states have enacted their own measures, such as California’s Delete Act, which grants residents the right to request the deletion of personal information from data brokers, a federal law encompassing these measures is still awaited. The American Privacy Rights Act, a bipartisan bill currently in Congress, aims to address these issues but has raised concerns about the potential preemption of stronger state laws.
A comprehensive federal privacy law would streamline regulations across states, ensuring consistency in how data breaches are reported and managed. However, it is crucial that such legislation builds upon, rather than undermines, the robust protections already in place in certain states. The goal should be a harmonized framework that enhances consumer rights, mandates timely breach notifications, and imposes stringent penalties for non-compliance. As the debate over federal privacy legislation continues, stakeholders must work together to craft laws that effectively safeguard consumers’ data in this digital age.
Consumer Protection Measures
Checking Web Service Security
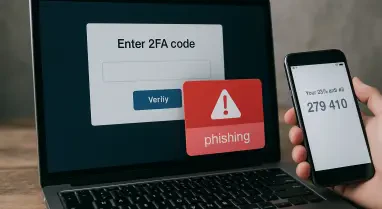
The analysis provides actionable advice for consumers to protect themselves in an increasingly hazardous digital environment. One of the first steps is to check if a web service is secure before engaging with it. Consumers are advised to use strong, unique passwords for different accounts and to enable two-factor authentication wherever possible. Two-factor authentication adds an extra layer of security, making it harder for cybercriminals to gain unauthorized access to accounts even if they obtain the password.
Furthermore, it’s essential for consumers to verify that websites they use are equipped with security certifications and encryption protocols. Look for “https://” in the URL and check for security seals from recognized organizations. Staying informed about a company’s breach history can also aid in making safer choices about which services to trust. Consumers should prioritize services that are transparent about their security practices and have a track record of prompt and effective breach responses.
Responding to a Data Breach
If a consumer receives notification of a data breach, it’s vital to take immediate and comprehensive actions to mitigate the potential damage. First, carefully read the notification letter to understand the scope of the breach and the types of information compromised. Next, consider freezing your credit to prevent identity theft and unauthorized financial activities. Resetting passwords for affected accounts, especially those using similar credentials, is another crucial step.
Additionally, enrolling in credit monitoring services can provide ongoing surveillance of credit activities and alert consumers to suspicious actions. Using password managers can help create and store complex passwords securely, reducing the risk of password-related breaches. Consumers should also consider opting out of data collection practices and requesting the deletion of unnecessary personal information held by companies. Taking these proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of further exploitation and protect individuals from the long-term consequences of data breaches.
In summary, the analysis compiles insights on the alarming rise of data breaches in 2024, examining affected industries, evolving cyberattack methods, and regulatory challenges. It emphasizes the criticality of awareness and proactive measures in safeguarding personal information. The analysis urged industries, regulators, and consumers to continually adapt to the dynamically changing cybersecurity landscape to mitigate these ever-present threats.